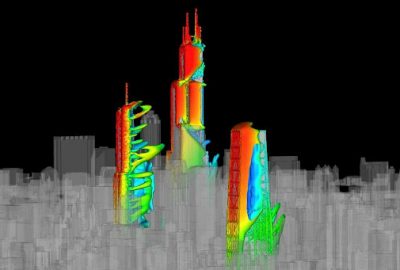
CFD
Objetivo Marte has a Commitment To R&D
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) is a powerful tool in understanding many complex phenomena. Furthermore, a detailed description of how a fluid flow behaves is only possible by solving a coupled non-linear Partial Differential Equations (PDE) system. The PDE system represents a set of conservations such as mass, momentum, energy, chemical species, turbulence, or any other quantity. Firstly, equations are spatially discretized and transformed into a Linear Algebraic Equation (LAE) system and then iteratively solved.
A general Conservation Equation (CE) takes the form:
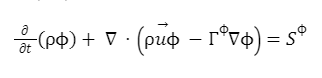
Where is the transported property (such as mass, velocity, temperature, O2, CO2 or any other quantity). In solving any PDE, a set of Boundary Conditions (BC) is required. Those are responsible for prescribing the flow behavior inside the domain of interest.
The steps to perform a CFD analysis are:
- All process starts with the geometry (such as a room, a car, a spacecraft, or any domain of interest) development in any Computer-Aided Design (CAD) software.
- Then, the space where the fluid will flow is discretized, i.e., divided into small volumes where the CE will take place to respect those physical phenomena. This step is known as meshing and is one crucial step since it is already linked to the models and schemes that will be applied in the next step. It is good practice to perform an independent mesh analysis, i.e., confirm that the results are independent of the mesh. It implies iterating between this step and the following ones to confirm this.
- At this point, the choice of models, numerical schemes, and equations to be solved is taken. This set of choices is also an essential step, and it requires a profound knowledge of the assumption taken underneath each model. Each scheme is related to the stability during convergence, implications in the results, and their applicability to each model. CFD software already has the equation discretization implemented, and the user choices are applied to the mesh, so the set of LAE may be solved.
- Post-processing is required to verify the results calculated in the previous step. In this step, the conclusions about our problem and how well the implementations along all previous steps are. For that reason, validation is usually taken before any extrapolation to the problem of interest. A known similar problem or an experimental quantification is used as a reference and compared with the results obtained. It allows confirming the applicability of the models using the similitudes of results.